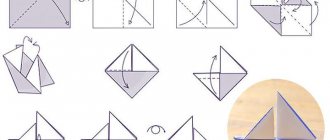
Artistic design from natural materials in kindergarten
A variety of natural materials are widely used in the constructive activities of preschool children. The main task of the teacher is to teach to feel the specificity of natural material, to see the diversity of its colors, shapes, textures and on this basis to create a variety of artistic images.
The implementation of tasks, on the one hand, develops imagination and creativity, on the other hand, leads children to master a generalized method of constructing an image based on clarity.
In studies of the development of considerations in preschool children, O. M. Dyachenko identifies two main qualitatively different methods of action for constructing an imaginary image:
1) “objectification”, when a child sees a certain object in an unfinished drawing;
2) “inclusion”, when the figure specified in the drawing turns into a secondary element of the imaginary image.
For the development of creative imagination it is fundamentally important:
- develop in children the ability to analyze material, first as the basis of a future image created by the “objectification” method, then as a detail significant for constructing a holistic image using the “inclusion” method;
- to develop such design skills and techniques as “completing” the image, “changing the spatial position”, “removing unnecessary things”, “combining”.
Main tasks of the first stage of training
constructive skills in making crafts from natural materials:
- develop the ability to analyze natural material as the basis for a future craft (select roots, branches, twigs);
— teach three basic techniques for constructing an image using the “objectification” method: the ability to change the spatial arrangement, complete construction, and remove unnecessary things.
The “objectification” method is fundamental, since it allows you to develop the ability to see the whole before the parts.
1st-2nd lessons:
— consideration of natural material;
— highlighting various images in configurations;
— construction of two or three images on one basis.
3-4th lessons:
- tasks of a problematic nature are given: the task is to create crafts based on a given basis;
— new materials are offered: pieces of tree bark of different sizes and configurations, dry tree mushrooms (as a base).
5-6th lessons:
- design is carried out according to plan.
Having determined the idea, children independently select natural materials: large ones are used as the basis of the craft, small ones are used as details.
At the second stage
The following main tasks are solved:
- develop the ability to build an image using the “inclusion” method;
- analyze natural material not only as the basis of a future craft, but also as a detail significant for constructing a holistic image (the same material can be both the basis of a craft and its detail).
1st lesson: design according to your own plans from material collected during the excursion.
2nd lesson: design according to your own design from a certain natural material obtained as an element of a future craft;
3rd lesson: completing the construction of a figure based on cross-shaped sticks-twigs;
Lesson 4: completing a figure based on two connected acorns, alder cones on a branch, straw tied in a certain place, pieces of bark with a stick fixed in the center.
Main tasks of the third stage
:
— expand the basic ways and techniques of building an image;
- to develop the ability to implement a plan, taking into account the general plot, detailing and enriching the image, and the specifics of the natural material.
Learning to design according to your own plot is the main goal.
1st-2nd lessons:
- constructing an invented fairy tale or story based on the plot.
Artistic design from natural materials
Middle group
Main goals
- develop the ability to analyze natural materials as the basis for future crafts;
— teach three basic techniques for constructing an image using the “objectification” method: changing the spatial arrangement, completing construction, removing unnecessary things.
Technical skills of children
Fastening with plasticine; fastening with glue.
Teacher's help
Helps to break off and cut off excess parts; helps attach additional parts, deepen the gap (mouth, beak).
Material for work
Roots, branches, twigs, pieces of tree bark, dry tree mushrooms, small natural material.
Senior group
Main goals
- develop the ability to build an image using the “inclusion” method;
- to develop the ability to analyze natural material not only as the basis of a future craft, but also as a detail significant for constructing a holistic image, by including it in this integrity;
— expand the basic ways and techniques of building an image;
- develop the ability to implement a plan.
Technical skills of children
Fastening with plasticine; fastening with glue; fastening with colored thin wire.
Teacher's help
Working with an awl; working with a knife; varnishing
Material for work
Cones, acorns, chestnuts, shells, alder cones on a branch, straw, bark, small natural material.
Stages of introducing natural material
Stages of introducing natural material in the middle group:
1st stage
Type of material:
roots, branches, twigs, small natural material.
2nd stage
Type of material:
pieces of tree bark of various sizes and configurations, dry tree mushrooms, small natural material.
Method of action
“Objectification”: change in spatial arrangement; completion; removing excess.
Stages of introducing natural material in the senior group:
3rd stage
Type of material:
cones, acorns, chestnuts, shells, small natural material.
Method of action
“Inclusion”: the use of natural material not only as the basis for a future craft, but also as part of the whole; multifunctional use.
4th stage
Type of material
: two sticks-twigs, fastened in the middle.
Method of action
Completing the figure.
5th stage
Type of material: two connected acorns, alder cones on a branch, straw tied in a certain place, pieces of bark with a stick fixed in the center.
Method of action
Completing the figure.
6th stage
A variety of natural materials.
Method of action
Application of all methods.
Design in kindergarten: approximate long-term calendar planning / ed. T. A. Kruglenya. – 2nd ed. – Minsk: Zorny Verasok, 2022. – 67 pp., pp. 12-14.
Owl
Objectives: To expand children's understanding of the use of non-traditional natural material - pine cones for making various crafts in combination with other traditional materials; promote the development of the desire to independently design crafts; use assessment of children's work as a teaching tool.
Material: Pine cones, colored paper: yellow, black, white, red or yellow gouache paint, black cardboard paper, a small piece of wool thread, a branch (for the stand).
Birds Objectives: Develop the ability to work on one creative task in a group or subgroup, but at the same time perform one specific task; develop the ability to observe and analyze visual demonstration material offered by the teacher; Based on analysis and observation, determine (outline) the order of the upcoming work; promote a sense of collectivism in children; develop a positive attitude towards each other and living nature.
Materials: Spruce and pine cones, feathers, colored paper, gouache paint, foam for wings, twigs, walnuts, plasticine.
The importance of designing from natural materials
The natural world around us is rich, beautiful and infinitely diverse. Introducing a child into this world, revealing his uniqueness, teaching him to love and take care of nature is the task and duty of adults. This must be done as early as possible, from the child’s first steps on the ground. This is where the system of continuous environmental education should begin—from the sphere of preschool education.
The relevance of the topic I have chosen is as follows: humanity is the main factor in the emergence of environmental problems on the planet.
Only now is society beginning to understand that the problems that have arisen arose as a result of its own incorrect activities on Earth, and they will not disappear by themselves.
That it is necessary to direct all efforts to eliminate these problems, to preserve natural resources, those riches of nature that people simply cannot do without. And in order to competently help nature, first of all, we need environmental education.
Without certain knowledge of the ecological foundations and laws of nature, a person will not be able to help nature, or even harm it even more with his illiteracy.
That is why it is so necessary to introduce children to nature as early as possible, to instill a love for it from a very early age, so that in the future they do not repeat the mistakes of modern society, and it, in turn, should try to normalize the current state of the natural environment for our children .
We can say that all this forms a single chain: we form an ecological culture in children from an early age, therefore, when they grow up, they will love, understand and, most importantly, take care of nature, and then there will be no environmental problems on the planet
All outstanding thinkers and teachers of the past attached great importance to nature as a means of raising children: Ya.A. Comenius saw in nature a source of knowledge, a means for the development of the mind, feelings, and will.
He attached great importance to nature and K.D. Ushinsky, he was in favor of “introducing children into nature,” in order to tell them everything accessible and useful for their mental and verbal development. Ideas by K.D. Ushinsky found further development in the works of E.N. Vodovozova, E.I. Tikheyeva, who paid a lot of attention to nature as a means of mental education of preschool children,
E.N. Vodovozova reveals the role of observation as the most accessible means of familiarizing young children with objects and phenomena of the surrounding nature. In her opinion, observation for children provides rich food for the development of the child's mind and aesthetic feelings.
E.I. Tikheyeva saw nature as a means of sensory education for children. Indeed, nature, as an inexhaustible source of forms, colors, sounds, can be widely used for the purpose of sensory education of preschool children.
A comprehensive study of the issues of sensory education of preschool children during productive activities, carried out under the leadership of A.V. Zaporozhets and A.G. Usova showed that training and the appropriate organization of visual activities, construction, work in nature, and didactic games have an effect in the sensory development of a child. Preschoolers consistently and purposefully learn the properties of objects - shape, size, color, density, etc., corresponding to perception skills.
A number of scientific works (A.I. Vasilyeva, N.K. Postnikova, I.A. Khaidurova, etc.) indirectly related to issues of sensory development of children show the importance of analyzing perception (the ability to see signs of natural objects) for the development of children’s activities in the process of cognition senior preschoolers' relationships in nature. That. Pedagogical work to familiarize preschoolers with nature reveals the possibility and necessity of developing sensory skills in children.
Baba Yaga
Objectives: Teach how to use natural materials to make crafts; develop fine motor skills of the hands; improve creativity; develop imagination, fantasy; to form compositional and aesthetic taste; promote the formation of curiosity and independence; cultivate perseverance, patience, accuracy in work; develop the ability to bring the work started to its logical conclusion;
to provide conditions for nurturing children's interest in arts and crafts and Russian folk tales.
Materials: Pine cones, pine needles, branches, coffee tin, twine, white and black paper, a small piece of fabric.
Topiary “Autumn”
Tasks:
Give an idea of the sequence of work on making topiary; teach the selection of materials for making an “autumn tree”; continue to develop skills in working with various natural and related materials:
to develop in children artistic taste, accuracy, precision, attention and creative exploration; develop hard work and mental activity; consolidate knowledge about the season - Autumn
Material: Pine cones, autumn tree leaves, rose hips, agrimony, flower pot.
Swans
Goal: To promote the development of cooperation skills in children; promote the development of their desire to focus together on a single topic, while performing one specific task; improve skills in constructive and modeling activities using natural and related materials; continue to work on improving the ability to plan a sequence of actions when performing a creative task. Cultivate hard work and the ability to finish what you start.
Material: Pine cone, white gouache paint, plasticine: white, red, black, cardboard paper or board (stand).
Preparation for work: Some natural materials require preliminary preparation, which parents do in advance, but you can involve children in this work, having previously explained to them what exactly needs to be done and how.
I hope that the presented material will be useful to you.