For every child, the preschool period is a very important time in life. At this time, the foundations of his future are laid, character is formed, health is strengthened, various vital skills and abilities are formed and consolidated, characteristics and talents are revealed, and personal training and education begins. That is why this period receives the most attention in modern pedagogical science and in its practical application in preschool institutions. For the full formation of a child’s personality and his all-round development, the interaction of kindergarten teachers with parents or guardians of pupils is of enormous importance.
Features of education and training of preschool children
Nature and evolution have decreed that a person gives birth to offspring that are physically and psychologically unprepared for independent existence. Unlike most animals, whose young are born fully formed and able to move, children of our species require the full attention of adults. Immediately after birth and until they reach several years of age, children cannot do without support and services. All this is provided to them by the family or structures that replace it.
A child’s personality is shaped by adults who are role models through upbringing and education. These are, first of all, immediate relatives - mothers, fathers, grandfathers and grandmothers, and then kindergarten teachers. They are the ones who are next to the kids in the first, most important years of their lives. Therefore, both the family and the kindergarten have a huge influence on the upbringing and education of preschool children. In order to get a full-fledged person with strong mental and physical health, excellently prepared for future life, the activities of parents and kindergarten teachers must be coordinated and integral. This is what the interaction between the two most important “branches of education” - family and social - serves.
“Interaction of the teacher with parents and employees of preschool educational institutions” - presentation
“Interaction of the teacher with parents and employees of the preschool educational institution”
Interaction of teachers with parents presupposes mutual assistance, mutual respect and trust, knowledge and consideration by the teacher of the conditions of family education, and by parents - of the conditions of education in kindergarten. It also implies a mutual desire of parents and teachers to maintain contact with each other. At the present stage, family education is recognized as leading, which is reflected in Art. 18 of the Law of the Russian Federation “On Education”.
establishing partnerships between participants in the pedagogical process, involving parents in the life of the kindergarten.
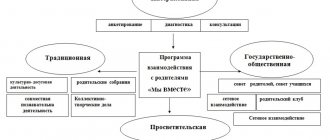
traditional non-traditional forms
collective - parent meetings (both group meetings are held 3-4 times a year, and general meetings with all parents of pupils at the beginning and end of the year), group consultations, conferences; individual – individual consultations, conversations; visual – folders, stands, screens, exhibitions, photos, open days.
information and analytical; information and analytical; leisure; leisure; educational; educational; visual information forms visual information forms.
aimed at identifying the interests and requests of parents, establishing emotional contact between teachers, parents and children. From the questionnaires, teachers learn the characteristics of preschoolers, what the child likes, dislikes, his preferences, what to name the child. This also includes surveys, tests, “Mailbox”, information baskets where parents can place questions that concern them.
joint leisure; holidays; Exhibitions; games; fashion show of costumes and others.
parent meetings in a non-traditional form (“KVN”, “Pedagogical Field of Miracles”, “Theater Friday”, “Pedagogical Case”, “What, where when?”, “Round table”, “Talk show”, “Helpline”, "Quizzes"); group consultations
informational and educational; informational and educational.
open days; watching videos; exhibitions of children's works; joint exhibitions of children's drawings and photographs on the theme “My family on vacation”, “Crafts made from natural materials”; others, including using ICT.
publishing a newspaper for parents; computer presentation of text, drawings, diagrams; libraries for parents on the main problems of family pedagogy; information stands; master classes on various topics; participation of parents in the educational process, in the development of the institution; organization of parent interest clubs.
drawing on the topic: “What kind of mother am I?”; formulation of your concept of education; analysis of one’s own pedagogical findings and failures; exchange of experience among like-minded people; creating a book about your child with his self-portrait on the cover; project method (parents are involved in completing a certain part of a common task together with their child, for example, introducing preschoolers to their hometown).
analysis of pedagogical situations; analysis of one’s own educational activities; solving pedagogical problems; game modeling of behavior.
questions for parents in connection with the material presented; raising discussion questions; proposal for discussion of two different points of view; giving examples.
The practice of working in preschool educational institutions proves the advantage of using active forms of work. With systematic group interaction, parents develop a culture of communication and independent thinking. Parents feel like active participants in the educational and educational processes. Creatively organized work directs parents to use their knowledge in specific situations and helps to conduct self-analysis of activities.
The interaction of teachers and parents in a preschool educational institution is carried out in a variety of forms - both traditional and non-traditional. In the process of different forms, methods of activating parents and methods of forming pedagogical reflection are used.
Features of project activities in preschool education
The project method is considered as a way of organizing the educational process, based on the interaction of teachers, students and their parents, a way of interacting with the environment, and step-by-step practical activities to achieve the goal.
The American educator and philosopher J. Dewey founded the project-based teaching method, the essence of which is briefly expressed by the slogan “Learn by doing.” According to him, the educational process should be built around a specific problem, the solution of which is relevant and significant for the child at the moment. The external result will be visible, understandable and applicable in practice. The internal result - the experience of activity - becomes an invaluable asset of the student, connecting knowledge and skills, competencies and values.
The main goal of the project method is to give children the opportunity to independently acquire knowledge by solving practical problems or problems. The topic chosen for the project is projected by the teacher onto all educational areas offered by the Federal State Educational Standard and onto various types of children's activities. This ensures the integrity of the educational process. Integration of knowledge from different thematic areas forms a holistic vision of the world around us, develops the child’s cognitive interest, allows him to “live” the topic in different types of activities (thinking, speech, work, creativity, etc.), absorb more information, understand the connections between subjects and phenomena and get tangible results. So, project activity is a special type of intellectual and creative activity; a set of techniques and operations for mastering a certain area of practical or theoretical knowledge, one or another activity; a way to achieve a didactic goal through a detailed development of a problem (technology), which should result in a very real, tangible practical result, formalized in one way or another.
A feature of project activities in the preschool education system is that the child cannot yet independently find contradictions in the environment, formulate a problem, or define a goal (idea). Therefore, in the educational process of ECE centers, project activities are collaborative in nature, in which children and teachers of the ECE center, as well as parents, participate. The degree of children’s participation in project activities depends on their age characteristics: in younger groups, children observe the activities of the teacher and parents, in middle age, children begin to participate in the implementation of the project, in older age they are full participants in the project.
Joint projects between kindergarten and family are especially important, as they allow “to create a natural situation of communication and practical interaction between children and adults (including parents).”
The experience of collective creativity is carried out against the background of general positive emotional experiences, which contributes to the development of friendly relations between children.
Children feel unhappy when they are outside the group. Therefore, pair, group and frontal projects are necessary for the development of children.
A paired project is carried out by a pair(s) of participants. Children acquire cooperation skills, learn to act together in the same space, solve a common problem, and choose adequate ways to solve it. A group project is carried out by a group of participants (from 3 to 10-12 people).
The principle of social partnership as a new philosophy of interaction between preschool educational institutions and families
A preschool organization as an organizational system is characterized by openness and homogeneity of the factors of its internal environment, as well as connections with the external environment. The family, along with the state, acts as a subject of social order. Social contracting entities act as social partners of ECE centers.
The term “social partnership” appeared in Russia in connection with changes in forms of ownership. The original meaning of the term was that representatives of employers and employees should solve relationship problems through negotiations, find compromises and reach agreements on a mutually beneficial basis.
The spread of economic relations in all spheres of the state has expanded the conceptual apparatus of this term. According to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, social partnership is a system of relations between employees (representatives of employees), employers (representatives of employers), state authorities and local governments, aimed at ensuring coordination of the interests of employees and employers in regulating labor relations and other directly related to them relations (Article 23 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
According to economist B. M. Genkin, “social partnership is the ideology, forms and methods of coordinating the interests of social groups to ensure their constructive interaction.” Thus, an analysis of definitions shows that the concept of “social partnership” is based on the constructive interaction of participants. This basis is also reflected in definitions of social partnership in education.
The legal basis for social partnership in the field of education is the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the Law “On Education in the Russian Federation”, the Law of the Russian Federation “On Non-Profit Organizations”, the Law of the Russian Federation “On Public Associations”, Decree of the President of the Russian Federation dated August 31, 1999 No. 1134 “On additional measures to support educational institutions in the Russian Federation.” At the municipal level, the legal basis for the organization of social partnership is made up of the federal laws “On local self-government in the Russian Federation”, “On the general principles of the organization of local self-government in the Russian Federation”, as well as the relevant laws of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, adopted in development of these federal laws. The educational standard for preschool education of the Federal State Educational Standard shows the importance of social partnership, explaining the basic principles of assistance and cooperation between children and adults in the process of child development and his interaction with people, culture and the outside world; introducing children to the sociocultural norms and traditions of the family, society and state.
The federal state standard of preschool education solves the problems of forming a common culture for pupils, interaction between educational and public associations, as well as the development of personal values and attitudes of pupils and students.
Within the framework of the model of preschool education (FSES DO), based on the Federal State Educational Standard (FSES DO), partnership means that the relationship of both parties is based on joint responsibility for the education of children. In addition, the concept of partnership implies that families and ECE centers are equal, have common goals and work together to achieve them